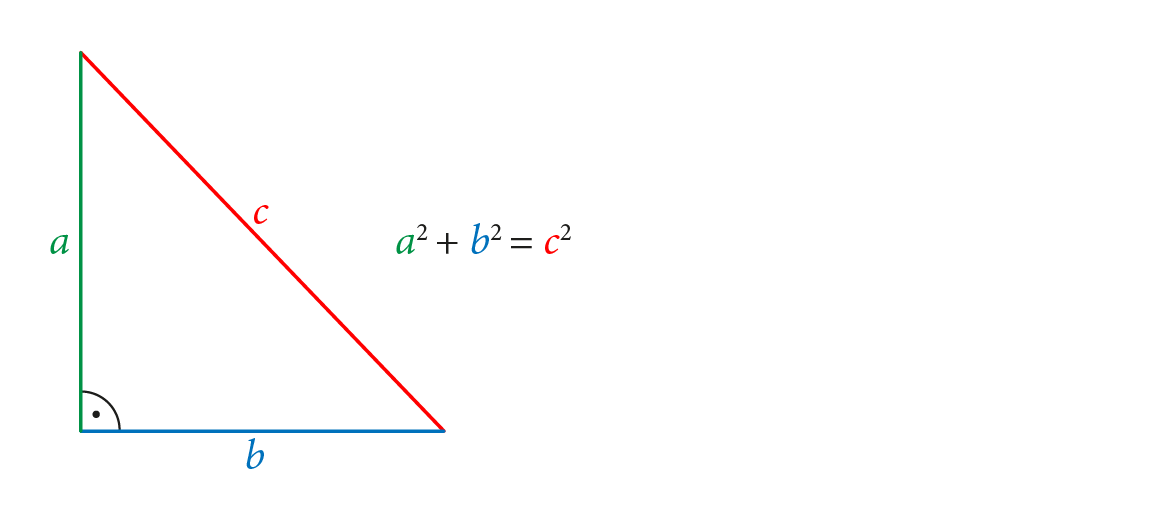Tożsamości trygonometryczne – kąty ostre
Tożsamości trygonometryczne to związki między funkcjami trygonometrycznymi.
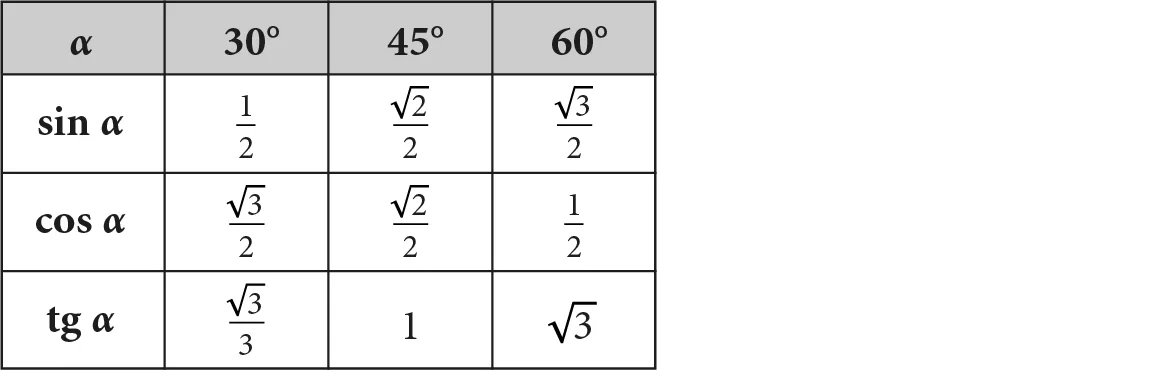
Dla dowolnego kąta ostrego\alpha α prawdziwe są zależności:
1.\mathrm{\sin ^{\mathrm{2}}}\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }+\cos ^2\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }=1, sin2 α + cos2 α = 1, jedynka trygonometryczna
Uwaga:\textcolor{#005FD4}{\mathrm{\sin ^2}\alpha =\left(\mathrm{\sin }\alpha \right)^2,} sin2 α = (sin α)2, \textcolor{#005FD4}{\mathrm{\cos ^2}\alpha =\left(\mathrm{\cos }\alpha \right)^2} cos2 α = (cos α)2
Np.\mathrm{\sin ^2}\textcolor{#E94D00}{12^{\circ }}+\cos ^2\textcolor{#E94D00}{12^{\circ }}=1 sin2 12∘ + cos2 12∘ = 1
2.\mathrm{\tg }\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }=\frac{\mathrm{\sin }\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }}{\mathrm{\cos }\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }} tg α = sin αcos α
Np.\mathrm{\tg }\textcolor{#E94D00}{62^{\circ }}=\frac{\mathrm{\sin }\textcolor{#E94D00}{62}^{\textcolor{#E94D00}{\circ }}}{\mathrm{\cos }\textcolor{#E94D00}{62}^{\textcolor{#E94D00}{\circ }}} tg 62∘ = sin 62∘cos 62∘
3.\mathrm{\sin }\mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }\mright)=\cos \textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha } sin(90∘ − α) = cos α
Np.\mathrm{\sin }75^{\circ }=\sin \mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{15^{\circ }}\mright)=\cos \textcolor{#E94D00}{15^{\circ }} sin 75∘ = sin(90∘ − 15∘) = cos 15∘
4.\mathrm{\cos }\mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }\mright)=\sin \textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha } cos(90∘ − α) = sin α
Np.\mathrm{\cos }85^{\circ }=\cos \mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{5^{\circ }}\mright)=\sin \textcolor{#E94D00}{5^{\circ }} cos 85∘ = cos(90∘ − 5∘) = sin 5∘
5.\mathrm{\tg }\mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }\mright)=\frac{1}{\mathrm{\tg }\textcolor{#E94D00}{\alpha }} tg(90∘ − α) = 1tg α
Np.\mathrm{\tg }80^{\circ }=\tg \mleft(90^{\circ }-\textcolor{#E94D00}{10}^{\textcolor{#E94D00}{\circ }}\mright)=\frac{1}{\mathrm{\tg }\textcolor{#E94D00}{10}^{\textcolor{#E94D00}{\circ }}} tg 80∘ = tg(90∘ − 10∘) = 1tg 10∘